
An undescended testicle in children is a common condition that often worries parents, especially when they notice one or both testicles missing from scrotum.
Many parents ask questions like:
What is the best age for surgery?
In this article, we will cover in detail the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and complications of undescended testicles, as well as their impact on fertility.
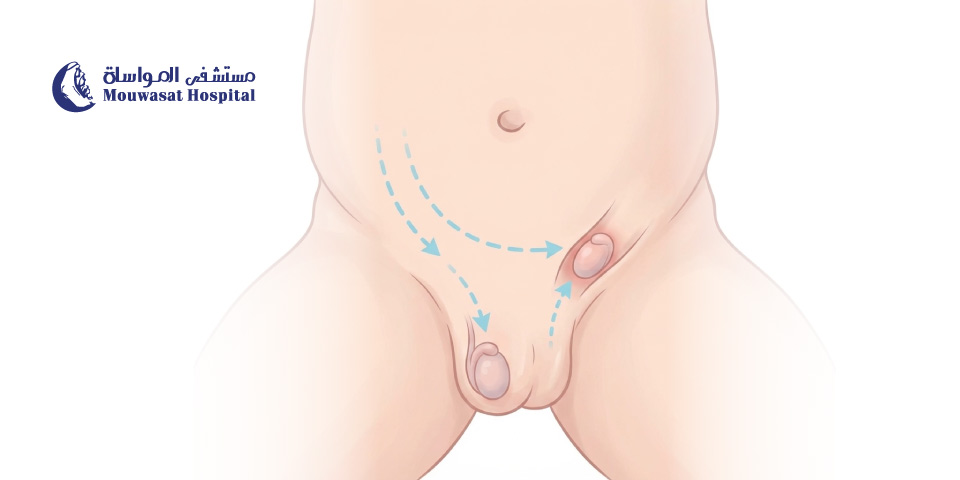
Before birth, the testicles develop inside the abdomen of a male fetus. Shortly before delivery, they move through the inguinal canal and descend into the scrotum. Normally, this process is completed before birth.
However, in some babies, especially those born prematurely, one or both testicles fail to descend and remain in the abdomen or groin. This condition is called undescended testicle or cryptorchidism.
In some cases, the testicle may descend naturally within the first six months of life. If not, medical intervention or surgery may be required to ensure the testicle is in its proper position.
The exact cause is unknown, but several factors may increase the risk:
Undescended testicles usually do not cause pain or urinary problems, but there are signs you can look for:
Sometimes the testicle appears and disappears, especially when the child is cold or upset, this is called a retractile testicle, which usually does not require surgery
If you notice any of these signs, consult a pediatrician for proper diagnosis and timely treatment. Add a link to “Pediatrician”, that take the audience to the Pediatric consultant's inner page
Doctors usually detect undescended testicles during a newborn’s physical exam. If your child has this condition, ask about follow-up visits. If the testicle has not descended by 3–4 months, it is unlikely to correct itself.
Older children may develop what appears to be a missing testicle later in life. This could indicate:
Seek medical advice immediately if you notice any changes in your child’s genital area.
Leaving the condition untreated can lead to serious health issues:
Fertility Problems: High abdominal temperature can damage sperm production, reducing future fertility.
Increased Risk of Testicular Cancer: Men with undescended testicles are more likely to develop testicular cancer, especially if both testicles are affected.
Testicular Torsion: A medical emergency requiring immediate surgery to prevent loss of the testicle.
Inguinal Hernia: Part of the intestine may push into the groin through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles, causing a painful bulge. Comment
Delayed Puberty: In some cases, undescended testicles can delay puberty signs.
Psychological Impact: May affect body image and self-confidence during adolescence.
If the testicle does not descend naturally within six months, medical intervention is necessary.
The Pediatric Surgery Department at Mouwasat Hospital offers comprehensive care for infants, children, and adolescents, including undescended testicle surgery. Key advantages include:
These features make Mouwasat Hospital a trusted choice for safe and effective pediatric surgeries.
Medical Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a pediatrician for diagnosis and treatment.
Not initially, but if left untreated, it can lead to infertility and increase the risk of testicular cancer.
Yes, sometimes within the first six months. If not, surgery is usually required.
Hormonal therapy is rarely used today due to low success rates. Surgery (orchiopexy) is the most effective treatment.
Between 6 and 18 months for optimal results and reduced complications.
About 30–60 minutes, and most children go home the same day.
General anesthesia with child-specific safety protocols.
Most children resume normal activities within 1–2 weeks.
Read more:
Umbilical Hernia in Children: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Inguinal Hernia in Children: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Laparoscopic gallbladder removal is one of the most advanced surgical techniques for treating gallbladder diseases. This minimally invasive procedure removes the affected gallbladder through small incisions in the abdomen. Compared to traditional open surgery, laparoscopic surgery offers greater precision, less pain,
faster recovery, and minimal scarring, making it the preferred choice for most cases.
Mouwasat Hospital provides robot-assisted laparoscopic gallbladder removal, combining the benefits of minimally invasive surgery with the enhanced accuracy of robotic technology.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a surgical procedure that removes the gallbladder using fine instruments and a small camera, giving the surgeon a clear view while minimizing incision size. This results in less pain and quicker recovery compared to open surgery.
Robotic gallbladder removal is an advanced technique where the surgeon controls a robotic system with high-definition 3D imaging and enhanced magnification. This ensures maximum precision, improved safety, and better outcomes, while reducing complications.
Gallbladder removal is recommended when medical treatment is not enough. Common conditions include:
In these cases, surgery is the best option to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
In rare cases, gallstones can be treated without removing the gallbladder using:
These methods are suitable only if:
However, these are temporary solutions since stones often recur and may cause complications. Laparoscopic gallbladder removal remains the safest and most effective option for permanent treatment.
Book a consultation with general surgeons
Before surgery:
Patients are admitted on the day of surgery or the day before
Fasting is required as per medical instructions
Preoperative checks are done by the care team
During surgery:
General anesthesia is administered so you are completely asleep and pain-free
The procedure usually takes about one hour
Laparoscopic steps include:
Open surgery may be necessary in complex cases such as severe infection or gallbladder rupture. Recovery after open surgery takes 4–6 weeks, compared to 1–2 weeks for laparoscopic or robotic surgery.
Robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgery offers:
This advanced technique ensures optimal safety and superior results, making it ideal for gallbladder removal.
Book your robotic gallbladder surgery now at Mouwasat Hospital
The liver continues to produce bile for fat digestion, but without storage in the gallbladder, bile flows directly into the intestine. Digestion remains normal, but fat intake per meal should be moderate. Following a healthy diet is essential.
Diet
Sleep
Physical Activity
Avoid Harmful Habits
Adhering to these guidelines prevents complications, speeds recovery, and ensures a safe return to normal life. Proper diet, early mobility, good sleep, and wound care reduce pain, prevent infections, and improve overall healing.
Mouwasat offers robotic and laparoscopic gallbladder surgery performed by highly experienced surgeons. Our advanced technology ensures precision, safety, and faster recovery for every patient.
Mouwasat Hospital offers the latest surgical technologies, including laparoscopic gallbladder removal and robotic-assisted surgery, ensuring the highest levels of precision, safety, and faster recovery with minimal pain.
Our team of highly experienced surgeons specializes in complex procedures using advanced equipment and robotic systems to deliver the best outcomes and enhance patient experience.
If you are looking for comprehensive care, accurate follow-up, and cutting-edge techniques like robotic surgery, Mouwasat Hospital is your ideal choice for a safe and quick recovery.
Yes. Laparoscopic gallbladder removal is the most common and preferred option because it involves small incisions, less pain, faster recovery, and lower risk of infection and scarring.
Most patients leave the hospital the same day or the next day and return to normal life within 1–2 weeks.
Open surgery is only necessary for complicated cases such as severe infections or tumors. It requires a larger incision, causes more pain, and involves a longer recovery period of 4–6 weeks, with a higher risk of infection and visible scars.
In general, if your condition allows, laparoscopic surgery is the best choice for quick recovery and minimal discomfort, while open surgery is reserved for medical necessity.
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, so you will be completely asleep and pain-free during surgery.
The operation usually takes about one hour, depending on your condition. Most patients are discharged the same day or the following day.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Please consult your doctor for personalized recommendations.
Success Stories in Robotic Surgery at Mouwasat:
Resources:
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy | Gallbladder removal - NHS | Robotic Cholecystectomy - University Surgeons Associates
A child’s natural curiosity often leads them to explore their surroundings and put objects in their mouth, exposing them to the risk of swallowing foreign bodies such as coins, button batteries, magnets, pins, beads, or small toy parts.
Therefore, foreign body ingestion is considered one of the most common pediatric emergencies. These objects can become a serious threat to a child’s life if not handled quickly and professionally.
If you notice that your child has swallowed a foreign object, go immediately to the pediatric emergency department for proper management.
When a child swallows a foreign object, it may lodge in the esophagus, stomach, or intestines, causing blockage, perforation, or internal bleeding.
In some cases, the object can enter the airway, leading to choking.
Certain objects, such as button batteries, magnets, or sharp items, can cause severe internal damage like poisoning or bleeding within a short time, making these cases medical emergencies that should never be delayed.
It can be a frightening moment when you notice your child put something in their mouth or suspect an object is missing. Watch for these warning signs:
Severe symptoms include intense pain, vomiting blood, breathing difficulty, or continuous coughing.
If you see your child swallow an object or notice these symptoms, go to the emergency department immediately.
At Mouwasat Hospital, our pediatric emergency department is available 24/7 with specialized teams and advanced equipment to handle these cases safely and quickly.
Consult Pediatric Experts at Mouwasat
Go to the pediatric emergency department immediately.
Coins are among the most commonly swallowed objects by children. Often, the coin passes through the stomach and intestines and exits naturally. However, sometimes it gets stuck in the esophagus or even the windpipe, posing serious risks such as:
If removed by a specialist within 24 hours, permanent damage is unlikely to happen. But prolonged retention can cause serious tissue injury.
Swallowing multiple coins containing zinc can lead to zinc poisoning, causing:
If your child swallows a coin, do not wait for complications; head to the emergency department immediately.
Button batteries are extremely dangerous and can cause internal burns and severe complications within hours.
Important steps for parents before heading to the ER:
Even if you only suspect ingestion, go to the emergency department immediately.
Small, high-powered magnets found in toys or household items can cause serious gastrointestinal injuries.
If multiple magnets are swallowed, they can attract each other through intestinal walls, causing blockage, perforation, or tissue erosion.
The risk is even higher if a magnet is swallowed with another metallic object like a battery.
If you suspect your child swallowed a magnet, especially more than one, or notice symptoms like abdominal pain, vomiting, fever, or irritability, go to the emergency department immediately.
X-rays will determine the location, and removal is usually done via endoscopy.
Sharp objects like pins or plastic fragments are among the most dangerous because they can puncture the esophagus, stomach, or intestines, leading to:
What to do:
Most cases require endoscopic removal, and in complex situations, surgery may be necessary.
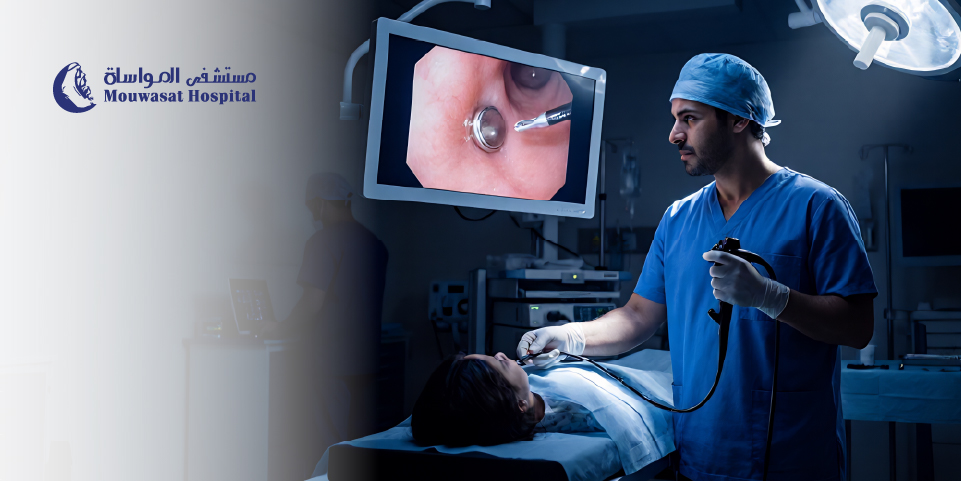
Foreign objects are often removed using endoscopy, a minimally invasive procedure.
A thin, flexible tube with a camera and light is inserted through the child’s mouth into the gastrointestinal tract.
The doctor visualizes the object and uses tiny instruments to remove it safely while checking for any tissue damage.
Our pediatric emergency department is equipped with technology and a multidisciplinary team, including pediatricians, gastroenterologists, and surgeons, to ensure rapid and safe intervention for emergencies such as:
We guarantee advanced, fast medical care for your child 24/7, because their safety is our top priority.
Prevention Is Better Than Cure, so keep your child’s environment safe: Remove small objects from their reach and choose age-appropriate toys without detachable parts, and supervise playtime to prevent accidents.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Please consult your doctor for personalized recommendations.
Resources:
A Child Swallows an Object—Children's Health | Swallowed a Coin—Poison Control | Button Battery Ingestion—EPBA
A child’s natural curiosity often leads them to explore their surroundings and put objects in their mouth, exposing them to the risk of swallowing foreign bodies such as coins, button batteries, magnets, pins, beads, or small toy parts.
Therefore, foreign body ingestion is considered one of the most common pediatric emergencies. These objects can become a serious threat to a child’s life if not handled quickly and professionally.
If you notice that your child has swallowed a foreign object, go immediately to the pediatric emergency department for proper management.
When a child swallows a foreign object, it may lodge in the esophagus, stomach, or intestines, causing blockage, perforation, or internal bleeding.
In some cases, the object can enter the airway, leading to choking.
Certain objects, such as button batteries, magnets, or sharp items, can cause severe internal damage like poisoning or bleeding within a short time, making these cases medical emergencies that should never be delayed.
It can be a frightening moment when you notice your child put something in their mouth or suspect an object is missing. Watch for these warning signs:
Severe symptoms include intense pain, vomiting blood, breathing difficulty, or continuous coughing.
If you see your child swallow an object or notice these symptoms, go to the emergency department immediately.
At Mouwasat Hospital, our pediatric emergency department is available 24/7 with specialized teams and advanced equipment to handle these cases safely and quickly.
Consult Pediatric Experts at Mouwasat
Go to the pediatric emergency department immediately.
Coins are among the most commonly swallowed objects by children. Often, the coin passes through the stomach and intestines and exits naturally. However, sometimes it gets stuck in the esophagus or even the windpipe, posing serious risks such as:
If removed by a specialist within 24 hours, permanent damage is unlikely to happen. But prolonged retention can cause serious tissue injury.
Swallowing multiple coins containing zinc can lead to zinc poisoning, causing:
If your child swallows a coin, do not wait for complications; head to the emergency department immediately.
Button batteries are extremely dangerous and can cause internal burns and severe complications within hours.
Important steps for parents before heading to the ER:
Even if you only suspect ingestion, go to the emergency department immediately.
Small, high-powered magnets found in toys or household items can cause serious gastrointestinal injuries.
If multiple magnets are swallowed, they can attract each other through intestinal walls, causing blockage, perforation, or tissue erosion.
The risk is even higher if a magnet is swallowed with another metallic object like a battery.
If you suspect your child swallowed a magnet, especially more than one, or notice symptoms like abdominal pain, vomiting, fever, or irritability, go to the emergency department immediately.
X-rays will determine the location, and removal is usually done via endoscopy.
Sharp objects like pins or plastic fragments are among the most dangerous because they can puncture the esophagus, stomach, or intestines, leading to:
What to do:
Most cases require endoscopic removal, and in complex situations, surgery may be necessary.
Foreign objects are often removed using endoscopy, a minimally invasive procedure.
A thin, flexible tube with a camera and light is inserted through the child’s mouth into the gastrointestinal tract.
The doctor visualizes the object and uses tiny instruments to remove it safely while checking for any tissue damage.
Our pediatric emergency department is equipped with technology and a multidisciplinary team, including pediatricians, gastroenterologists, and surgeons, to ensure rapid and safe intervention for emergencies such as:
We guarantee advanced, fast medical care for your child 24/7, because their safety is our top priority.
Prevention Is Better Than Cure, so keep your child’s environment safe: Remove small objects from their reach and choose age-appropriate toys without detachable parts, and supervise playtime to prevent accidents.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Please consult your doctor for personalized recommendations.
Resources:
A Child Swallows an Object—Children's Health | Swallowed a Coin—Poison Control | Button Battery Ingestion—EPBA
Laparoscopic gallbladder removal is one of the most advanced surgical techniques for treating gallbladder diseases. This minimally invasive procedure removes the affected gallbladder through small incisions in the abdomen. Compared to traditional open surgery, laparoscopic surgery offers greater precision, less pain,
faster recovery, and minimal scarring, making it the preferred choice for most cases.
Mouwasat Hospital provides robot-assisted laparoscopic gallbladder removal, combining the benefits of minimally invasive surgery with the enhanced accuracy of robotic technology.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a surgical procedure that removes the gallbladder using fine instruments and a small camera, giving the surgeon a clear view while minimizing incision size. This results in less pain and quicker recovery compared to open surgery.
Robotic gallbladder removal is an advanced technique where the surgeon controls a robotic system with high-definition 3D imaging and enhanced magnification. This ensures maximum precision, improved safety, and better outcomes, while reducing complications.
Gallbladder removal is recommended when medical treatment is not enough. Common conditions include:
In these cases, surgery is the best option to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
In rare cases, gallstones can be treated without removing the gallbladder using:
These methods are suitable only if:
However, these are temporary solutions since stones often recur and may cause complications. Laparoscopic gallbladder removal remains the safest and most effective option for permanent treatment.
Book a consultation with general surgeons
Before surgery:
Patients are admitted on the day of surgery or the day before
Fasting is required as per medical instructions
Preoperative checks are done by the care team
During surgery:
General anesthesia is administered so you are completely asleep and pain-free
The procedure usually takes about one hour
Laparoscopic steps include:
Open surgery may be necessary in complex cases such as severe infection or gallbladder rupture. Recovery after open surgery takes 4–6 weeks, compared to 1–2 weeks for laparoscopic or robotic surgery.
Robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgery offers:
This advanced technique ensures optimal safety and superior results, making it ideal for gallbladder removal.
Book your robotic gallbladder surgery now at Mouwasat Hospital
The liver continues to produce bile for fat digestion, but without storage in the gallbladder, bile flows directly into the intestine. Digestion remains normal, but fat intake per meal should be moderate. Following a healthy diet is essential.
Diet
Sleep
Physical Activity
Avoid Harmful Habits
Adhering to these guidelines prevents complications, speeds recovery, and ensures a safe return to normal life. Proper diet, early mobility, good sleep, and wound care reduce pain, prevent infections, and improve overall healing.
Mouwasat offers robotic and laparoscopic gallbladder surgery performed by highly experienced surgeons. Our advanced technology ensures precision, safety, and faster recovery for every patient.
Mouwasat Hospital offers the latest surgical technologies, including laparoscopic gallbladder removal and robotic-assisted surgery, ensuring the highest levels of precision, safety, and faster recovery with minimal pain.
Our team of highly experienced surgeons specializes in complex procedures using advanced equipment and robotic systems to deliver the best outcomes and enhance patient experience.
If you are looking for comprehensive care, accurate follow-up, and cutting-edge techniques like robotic surgery, Mouwasat Hospital is your ideal choice for a safe and quick recovery.
Yes. Laparoscopic gallbladder removal is the most common and preferred option because it involves small incisions, less pain, faster recovery, and lower risk of infection and scarring.
Most patients leave the hospital the same day or the next day and return to normal life within 1–2 weeks.
Open surgery is only necessary for complicated cases such as severe infections or tumors. It requires a larger incision, causes more pain, and involves a longer recovery period of 4–6 weeks, with a higher risk of infection and visible scars.
In general, if your condition allows, laparoscopic surgery is the best choice for quick recovery and minimal discomfort, while open surgery is reserved for medical necessity.
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, so you will be completely asleep and pain-free during surgery.
The operation usually takes about one hour, depending on your condition. Most patients are discharged the same day or the following day.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Please consult your doctor for personalized recommendations.
Success Stories in Robotic Surgery at Mouwasat:
Resources:
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy | Gallbladder removal - NHS | Robotic Cholecystectomy - University Surgeons Associates
Acid reflux in infants and children is one of the most common health issues during the early years of life. Many babies encounter food or milk being regurgitated back into the esophagus from the stomach, and this problem may not go away. in older children, causing concern for parents.
In this comprehensive guide, we will cover the causes of acid reflux in babies and children, its symptoms, and the different treatment methods. We will also answer frequently asked questions such as:
Acid reflux occurs when stomach contents flow back into the esophagus, the tube that connects the mouth to the stomach, causing what is known as acid regurgitation. This condition can irritate the esophagus and lead to heartburn.
Acid reflux in infants and children is common across all age groups, from newborns to older kids. However, when reflux happens frequently, it becomes a chronic condition called Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), which can cause more severe symptoms.
When food is swallowed, it travels from the mouth to the stomach through the esophagus. A muscular valve at the lower end of the esophagus (called the lower esophageal sphincter) prevents food from flowing back. If this valve does not close properly, stomach contents can return to the esophagus.
In infants, this muscle is underdeveloped, making reflux common. That’s why most babies spit up milk after feeding. Acid reflux usually disappears by the age of one as the muscle matures.
However, if symptoms persist or worsen, it may indicate GERD.
Reflux in babies and children can be mild or severe, and each has distinct symptoms:
This condition is more serious and requires medical attention. Common symptoms include:
If these symptoms occur repeatedly, consult a pediatrician for proper diagnosis and treatment.
If symptoms are mild, tests may not be necessary. However, persistent or severe symptoms may require:
These tests help determine the severity and guide treatment, especially if weight loss or complications occur.
After diagnosis, the doctor will choose the appropriate treatment based on severity:
Never use medication without a doctor’s guidance.
In severe cases that do not respond to medication, or when serious complications arise, surgery may be recommended.
The goal is to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter to prevent food and acid from flowing back. This is an option when medications fail or complications occur.
Fundoplication: The most common procedure, where the upper part of the stomach is wrapped around the esophagus to reinforce the valve.
Methods include:
Laparoscopic fundoplication is the most popular choice because it involves smaller incisions, less pain, faster recovery, and minimal scarring.
Most children recover well, but some may need additional surgery if the wrap is too tight or too loose.
The Pediatric Surgery Department at Mouwasat Hospital offers comprehensive and personalized care for children suffering from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or cases requiring surgical intervention. The approach is holistic, starting from accurate diagnosis to post-treatment follow-up.
Key Advantages of Acid Reflux Treatment at Mouwasat Hospital
Reflux usually improves significantly between 6 to 12 months and often disappears completely by 12 to 18 months.
Food allergies or intolerances can increase reflux symptoms. The most common culprit is cow milk protein (not lactose), which is the leading cause of food-related reflux in infants.
Acid reflux surgery for children is generally safe, especially when performed laparoscopically by an experienced medical team in a well-equipped hospital like Al Mouwasat.
Potential risks are minimal and may include:
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified pediatric specialist for diagnosis and treatment.
Resources:
Gastroesophageal reflux disease | Anti-reflux surgery - children | Reflux in breastfed babies
Cleft lip and cleft palate are among the most common congenital birth defects. They appear as an opening or gap in the upper lip, the roof of the mouth (palate), or both, caused by incomplete fusion of facial tissues during the early weeks of pregnancy.
This condition not only affects facial appearance but can also lead to feeding difficulties, speech problems, and breathing issues. Early diagnosis and timely medical intervention are essential for improving outcomes.
Thanks to medical advancements, repairing and treating cleft lip and palate is now possible through specialized reconstructive surgeries and integrated treatment plans, giving children the chance to live healthy, normal lives.
Cleft lip and palate occur when facial and oral tissues fail to fuse completely during fetal development in the first weeks of pregnancy, resulting in a gap in the upper lip or palate.
Several factors contribute to this condition, including
Cleft lip and palate are usually visible at birth, but in some cases, they can be detected during pregnancy through ultrasound. The severity and type of cleft vary:
The severity ranges from a small notch in the lip to a gap extending through the lip, gum, and palate up to the base of the nose. These may occur alone or with other conditions.
Children with cleft lip or palate may face several complications requiring multidisciplinary care:
Children with cleft palate are more prone to fluid buildup in the middle ear, leading to frequent infections and hearing loss. Hearing tests are recommended at 4 weeks, then at 12 weeks, and annually during early childhood.
The palate plays a vital role in sound formation. Children with cleft palate may struggle to pronounce certain sounds and may develop nasal speech or unusual articulation even after surgery. Speech therapy is often needed post-surgery.
Missing teeth, extra teeth, or misaligned teeth are common, causing crowding or shifting. A dental visit is advised when the first teeth appear or before 18 months to prepare for future orthodontic treatment.
Infants may have difficulty breastfeeding or bottle-feeding due to the gap in the lip or palate. Special feeding bottles or guidance from a nutrition specialist may be required.
Cleft lip can often be detected during pregnancy through routine ultrasound, allowing parents to plan for care and treatment early.
Treatment focuses on specialized reconstructive surgery, usually involving a series of carefully planned procedures to:
With modern medical techniques, children who undergo comprehensive treatment programs can enjoy normal lives with restored function and appearance.
Treatment plans vary based on the size and location of the cleft and typically include:
The goal is to correct congenital deformities, restore speech and feeding functions, and improve facial aesthetics.
Procedure:
Anesthesia: General anesthesia for comfort and safety.
Incisions:
Surgeries may be combined or performed separately depending on the child’s age and condition.
Closure: Using absorbable or removable stitches.
Outcome: Hidden scars that fade over time, giving the child a natural appearance and normal function.
After surgery, some children may struggle to return to normal feeding, while others adapt quickly. Feeding usually resumes once the child wakes up, though initial discomfort is common.
After palate repair, sucking ability improves gradually. Parents may need to assist by gently squeezing the bottle until healing is complete.
Adults can undergo surgeries to close the gap and reshape the lip and face for normal appearance and oral functions like speech and eating.
Speech therapy
Dental and orthodontic treatment
Mouwasat Hospital offers comprehensive, personalized care for children with cleft lip and palate through a multidisciplinary approach, from accurate diagnosis to post-treatment follow-up.
Key Advantages:
At Mouwasat Hospital, we provide advanced surgical care and continuous follow-up to ensure the best outcomes for children and their families—from diagnosis to full recovery.
A personalized surgical plan is created based on the child’s condition and the severity of the cleft. Generally, the recommended ages for surgery are
Treatment is managed by a multidisciplinary medical team that provides a long-term care plan starting from birth and continuing until facial growth is complete during adolescence.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.
Read also:
Inguinal Hernia in Children: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
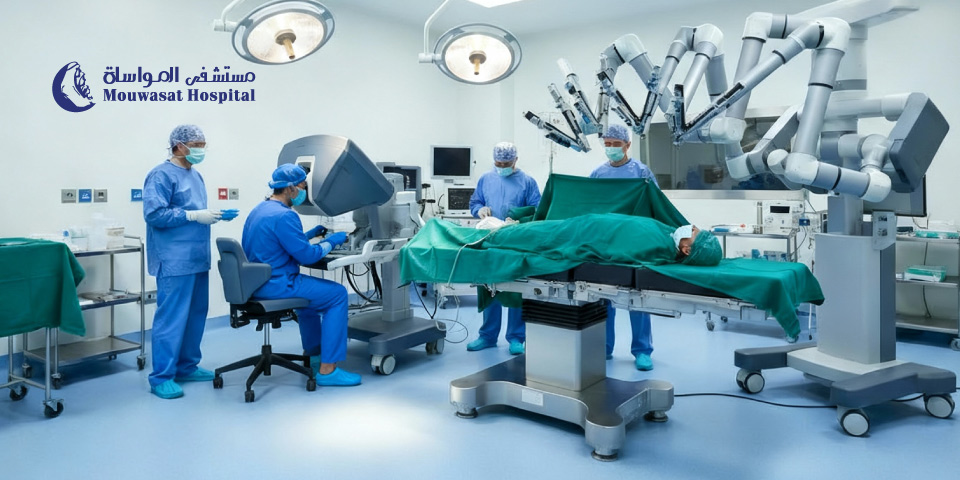
Robotic-assisted urologic surgery is one of the most advanced medical technologies, revolutionizing the treatment of urologic conditions. This approach uses a robotic surgical system controlled by the surgeon to perform procedures with exceptional precision while minimizing traditional surgical intervention.
Robotic urologic surgery at Mouwasat Hospital combines high accuracy, reduced complications, faster recovery, and numerous success stories of procedures performed using robotic technology.
A robotic surgical system is an advanced platform that enhances the surgeon’s capabilities through:
This technology allows surgeons to access hard-to-reach areas through tiny incisions, reducing pain, bleeding, and surgical risks.
Robotic surgery follows the same principles as traditional surgery but with a key difference: access and precision. Instead of a large incision, robotic-assisted surgery uses small incisions only a few millimeters wide, making it a minimally invasive approach. The process includes:
Important: The surgeon is in full control throughout the procedure. The robot is an advanced tool that provides greater precision, enhanced visualization, and access to deep anatomical areas without large incisions.
The system consists of the surgeon console, patient cart (where robotic arms and instruments are mounted), and vision cart, which provides real-time imaging for the surgical team. This setup ensures accuracy and stability in confined anatomical spaces, making it ideal for urologic surgeries.
Robotic-assisted uro;ogic surgery offers significant benefits over traditional methods, including:
For patients, these benefits translate into:
Robotic surgery is used for a wide range of urologic procedures, including:
Note: Our robotic surgery specialists at Mouwasat Hospital will determine whether robotic-assisted surgery is suitable for your condition after a comprehensive evaluation.
These surgeries are among the first of their kind in private hospitals in the Eastern Province, performed by the Robotic Surgery Center at Mouwasat Hospital, supported by advanced AI-driven services.
Our medical team at Mouwasat Hospital in Khobar successfully performed several complex robotic-assisted radical prostatectomies for patients with advanced prostate cancer, including bladder neck reconstruction.
This technique is currently the best option for complex cases compared to traditional open surgery or laparoscopy, offering:
Robotic surgery can also be used for other urologic procedures, such as partial or total kidney removal, adrenal gland surgery, bladder surgery, and ureteral reconstruction.
Discover more success stories: Robotic-assisted tumor removal while preserving kidney function for a 60-year-old patient at Mouwasat Hospital in Khobar.
Mouwasat Hospital uses the latest generation of the da Vinci robotic surgical system, the most widely adopted multi-port robotic platform in the world. It delivers proven capabilities across a broad range of procedures in multiple specialties.
The da Vinci robotic system at Mouwasat Hospital features advanced surgical instruments, high-definition 3D vision, and innovative technologies. These features provide exceptional flexibility, streamline instrument standardization, and enhance overall operating room efficiency.
Mouwasat Hospital was the first private hospital in Eastern Province to introduce robotic surgery using the latest da Vinci Xi system, reflecting our commitment to delivering world-class healthcare through cutting-edge technology.
Our team includes highly qualified Saudi and international experts in robotic surgery, ensuring:
Robotic surgery at Mouwasat is not limited to urology—it also covers:
Additionally, Mouwasat offers other robotic systems, including those for orthopedic surgery and knee replacement, with numerous successful cases demonstrating the accuracy and efficiency of robotic technology in improving surgical outcomes.
Book your consultation now with the specialized robotic surgery team at Mouwasat Hospital and find out if this advanced technology is the right choice for you.
No, the robotic system does not operate independently or make decisions. The surgeon is in full control throughout the procedure using a console that directs the robotic arms with extreme precision. The robot’s role is to enhance the surgeon’s capabilities by providing:
No, robotic surgery is not experimental. It is a proven, advanced technology that has been successfully used worldwide for over two decades. Systems like da Vinci® are utilized in thousands of hospitals globally and are considered the gold standard for many complex procedures across multiple specialties.
At Mouwasat Hospital, we use the latest generation of the da Vinci Xi robotic system to ensure maximum safety and precision, backed by a strong track record of successful surgeries and outstanding outcomes.
No, robotic surgery is not limited to complex cases. While it is highly effective for intricate procedures such as radical prostatectomy or kidney tumor removal, it is also an excellent option for many other surgeries, including general surgery, bariatric surgery, and more.
The key advantage of robotic-assisted surgery is its minimally invasive approach, which means smaller incisions, less pain, faster recovery times
Whether your procedure is simple or complex, the robotic surgery specialists at Mouwasat Hospital will determine the best approach for your condition after a thorough evaluation.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Please consult your physician for personalized recommendations.
Discover more success stories in robotic surgery
Resources:
Da Vinci Xi Robotic Surgical System | Robotics in urology - PMC | Robotic Surgery - UC Davis Health
A child falling on their head is one of the most stressful situations for parents. While it’s common during different stages of childhood, whether infants or toddlers learn to walk, play, or engage in sports.
Most head injuries are minor and don’t require panic. However, in some cases, they can be serious and lead to complications such as internal bleeding or concussion.
Statistics show that the risk of head injuries increases as children grow older, making prompt medical intervention crucial to avoid potential dangers.
we’ll explain the warning signs after a child falls on their head that require immediate emergency care and why you should never delay or rely solely on home observation
Head injuries in children vary in severity and type. They can range from minor bruises or superficial cuts to serious conditions like skull fractures or brain injuries. Generally, head injuries include any damage to the scalp, skull, or brain.
Most Common Types of Head Injuries in Children:
Symptoms vary depending on the severity of the injury but recognizing them helps you act quickly and protect your child.
Signs of Mild Injury:
Warning signs of moderate or severe head injury include the above symptoms, plus the following. Seek medical care or go to the ER immediately if any appear:
Call emergency services immediately if:
Repeated or persistent vomiting usually indicates a moderate or severe head injury and requires immediate medical attention.
Important: Do not wait if vomiting is accompanied by loss of consciousness, severe headache, or other warning signs; go to the ER immediately.
Monitor the child closely for 4 to 6 hours after the fall, even if no serious symptoms appear initially. This observation period helps detect delayed signs such as severe headaches, repeated vomiting, or behavioral changes.
If 6 hours pass without worrying about symptoms, the risk of serious injury is very low.
However, remain vigilant for 24 to 48 hours, as some symptoms may appear later.
Important: If any severe symptoms occur, such as loss of consciousness, extreme drowsiness, severe headache, repeated vomiting, seizures, or blood or fluid from the nose or ears, go to the ER immediately.
Consult Pediatric Specialists at Mouwasat Hospital
Our team of specialized doctors ensures rapid intervention and treatment for all emergencies.
Examples of Cases We Handle:
Our facilities include:
Your child’s safety is our top priority. We guarantee advanced and fast medical care at all times.
Resources:
HealthyChildren.org | Stanford Medicine Children's Health | American Academy of Pediatrics