Breast Cancer Awareness Month
Objectives:
Raising the public awareness, particularly women, about the risk factors that increase the possibility of developing breast cancer, methods of prevention, the importance of early detection, target groups, location of service center, and providing integrated service to fight breast cancer from detection to treatment.
Overview:
- Breast cancer is caused by the abnormal growth of breast cells.
- Having breast lumps does not necessarily mean that cancer is present; some lumps form due to cysts or infections.
- Diagnosing breast cancer is done by: Breast self-examinations, physical examinations, and mammograms respectively.
- Complications of breast cancer include the spreading of cancerous cells to neighboring tissues.
- Some of the most important ways to prevent breast cancer include, leading a healthy lifestyle, and breastfeeding.
Definition of cancer:
Cancer is a broad term given to a collection of related diseases characterized by the abnormal growth of tumors on the organs of the body. There are two types of tumors, benign tumors and malignant tumors (which are known as cancerous tumors). The two types are distinguished by examining the tissue (taking a sample).
Definition of Breast Cancer:
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops due to uncontrollable changes in the function or growth of the cells forming breast tissue. These changes transform these cells into cancerous cells that have the ability to spread. Breast cancer can occur in both men and women, but it is more common in women.
Statistic:
According to European and American studies, one in eight women is at risk of developing breast cancer at some point in her life.
Types of Breast Cancer:
There are several types of breast cancer, and the most common of these types is known as Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS): This type of cancer was named that way because it starts inside the milk ducts. This type accounts for 90% of breast cancer cases.
Causes:
The actual cause of breast cancer is not known, but there are some factors that increase the risk of developing breast cancer.
Symptoms:
In most cases there are no symptoms, but these signs may appear in advanced stages:
- A solid non-painful lump or node in the breast or the armpit.
- Breast tenderness and swelling.
- Breast discharge.
- Change in the size, shape or appearance of the breast or wrinkling in the skin of the breast
- A newly inverted nipple.
- Itching, or crusting or scaling of the skin surrounding the breast.
- In most cases the patient does not feel any pain.
Having breast lumps does not necessarily mean that cancer is present; some lumps form due to cysts or infections.
When to see a doctor:
- Upon noticing a persistent and solid lump.
- If the lump does not disappear within 4-6 weeks.
- Upon noticing skin changes.
- Upon noticing nipple discharge (usually blood).
- If a nipple gets inverted.
- Upon noticing a change in the size of the lymph nodes in the armpit (lump).
Diagnosis:
A) Breast self examination:
Breast self exams should be done routinely every month, three to five days after the menstrual cycle, and the doctor must be contacted immediately upon noticing any changes.
Breast self-examination methods:
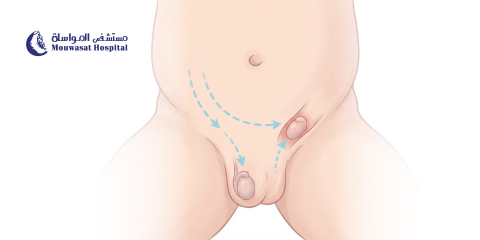
1- Lying down:
- Lie down on your back with a pillow under your right shoulder, then use the pads of the three middle fingers on your left hand to check the right breast.
- Press using light and firm pressure in a circle without lifting your fingers off the skin.
- Keep pressing your fingers in an up and down pattern.
- Feel for changes in the breast, above and below the collarbone and in the armpit.
- Repeat the previous steps on the left breast using your right hand.
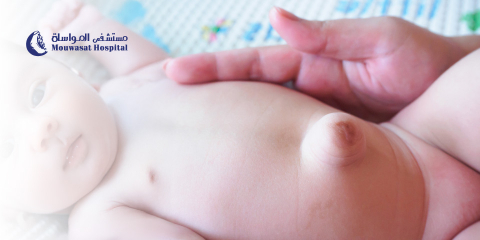
2- Standing in front of the mirror and noting any changes:
- Hold arms at your side
- Hold arms over your head.
- Press your hands on your hips and tighten your chest muscles.
- Bend forward with your hands on your hips.
B) Physical examination:
It is a breast exam conducted by trained doctors and specialists in the hospital. If a patient has a family history of breast cancer, the doctor will immediately recommend a mammogram.
C) Mammography (Mammogram)
Mammography is an x-ray imaging method used to examine the breast. It is the most accurate way to detect breast cancer early, even if it was small in size. This early detection could lead to faster recovery.
All women are advised to have mammograms at least once a year, starting at the age of 40 (and perhaps earlier if there is a family history of breast cancer).
Risk factors:
- Gender: Breast cancer can occur in both men and women, but it is more common in women.
- Advanced age: Especially over the age of 55 years.
- Medical family history and genetics: If any first-degree relatives were diagnosed with breast cancer due to genetic factors and not due to other reasons, then regular checkups for breast cancer and ovarian cancer must be done.
- Delayed pregnancy (after 30), or no pregnancy.
- Not Breastfeeding
- Reaching puberty at an early age (before 12).
- Beginning menopause at an older age (after 55).
- Some types of treatment, such as: Radiation therapy or hormone therapy or the use of hormonal contraceptives.
- Exposure to radiation at an early age (before 30).
- Personal history of malignant tumors in the breast or some types of benign tumors.
- Obesity and lack of physical exercise.
- Consuming alcohol.
Complications:
Untreated breast cancer can lead to:
- Ulcerations and inflammations in the skin.
- Cancerous cells start multiplying in the breast.
- The tumor can spread to the lymph nodes, which increases the risk of cancer spreading to other vital organs in the body (such as: the brain, liver, and lungs), which can affect the functions of these organs and stop them.
- The patient's health may severely deteriorate leading to death in advanced stages of the disease.
Treatment:
Treatment options depend on the diagnosis (type of tumor,stage, size) and the health status of the patient:
- Chemotherapy and biotherapy
- Radiation therapy.
- Hormone therapy.
- Surgery.
- Targeted therapy.
Prevention:
Primary prevention:
- Healthy lifestyle, which includes healthy food, physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Consult the doctor before using alternative hormones
- Make sure to breastfeed your baby.
- Avoid smoking.
- Early detection.
Secondary prevention:
- Breast self examination.